Understanding a Buzz Coil Wiring Diagram is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems that involve these specific components. Whether you're a hobbyist, a student, or a seasoned technician, having a clear grasp of the Buzz Coil Wiring Diagram can demystify complex circuits and ensure proper functionality.
What is a Buzz Coil Wiring Diagram?
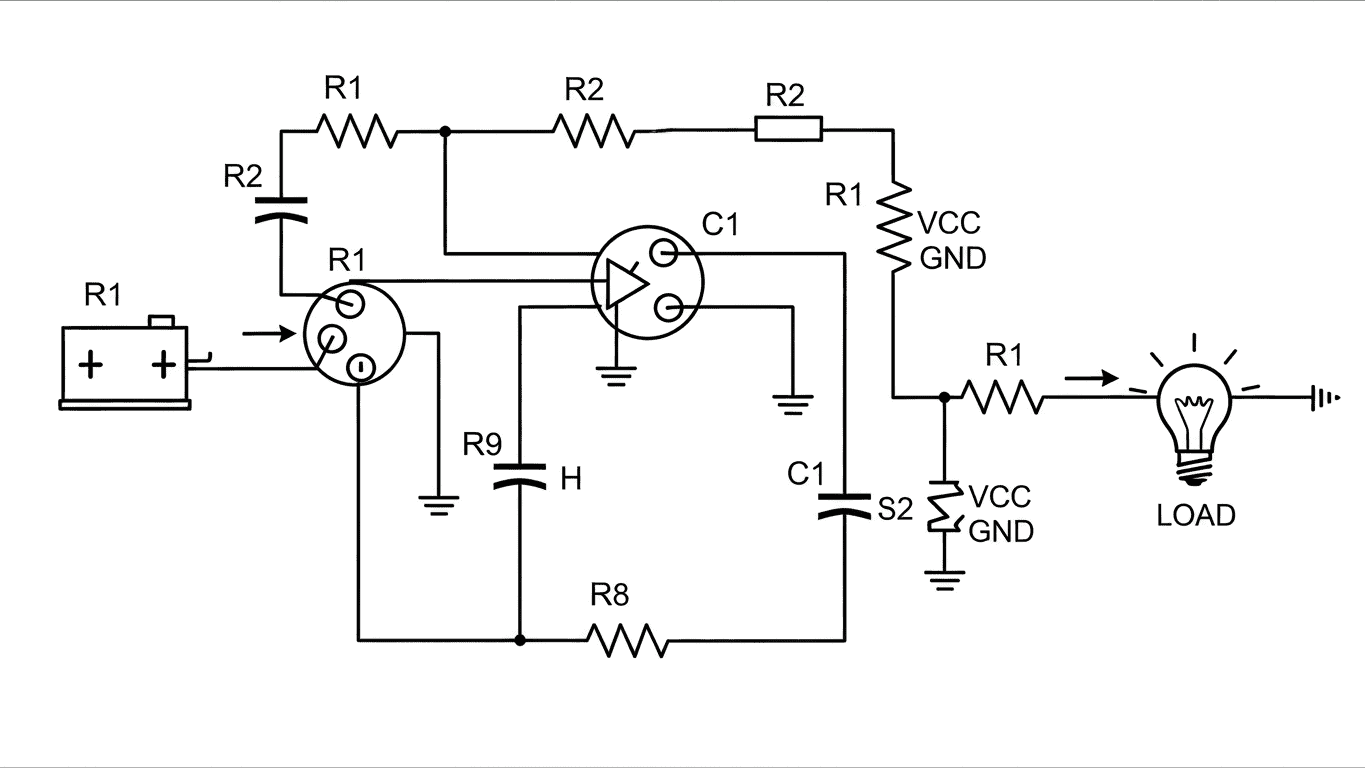
A Buzz Coil Wiring Diagram is a schematic representation that illustrates how the components of a buzz coil circuit are interconnected. A buzz coil itself is a type of induction coil used in early automobile ignition systems and other applications requiring a high-voltage spark. The diagram shows the flow of electricity through the primary and secondary windings of the coil, as well as associated components like interrupters, condensers, and power sources. It's essentially a roadmap for assembling, troubleshooting, or modifying these electrical setups. The proper interpretation of a Buzz Coil Wiring Diagram is paramount for safety and operational success .
These diagrams serve multiple vital purposes. For beginners, they provide a visual guide to understanding the fundamental principles of how a buzz coil works. For experienced individuals, they act as a reference for diagnostic purposes, allowing them to pinpoint faults or verify connections. The typical components you'll find depicted in a Buzz Coil Wiring Diagram include:
- The Buzz Coil itself (with primary and secondary windings)
- A DC power source (like a battery)
- An interrupter or commutator (to rapidly break and make the primary circuit)
- A condenser (to absorb excess voltage spikes)
- Spark gap or output terminal
The complexity of a Buzz Coil Wiring Diagram can vary. Simpler versions might show only the core coil and interrupter. More advanced diagrams might incorporate additional components for spark timing or power regulation. Here's a basic breakdown of how the connections generally flow:
- The DC power source is connected to the interrupter.
- The interrupter is then connected to the primary winding of the buzz coil.
- The other end of the primary winding is connected back to the power source, completing the primary circuit.
- The secondary winding, which has many more turns of wire, is where the high voltage is generated.
- The output of the secondary winding is typically connected to a spark gap where the ignition spark is produced.
A simplified representation can be seen in this table:
| Component | Connection Point |
|---|---|
| Power Source (+) | Interrupter Terminal A |
| Interrupter Terminal B | Buzz Coil Primary Terminal 1 |
| Buzz Coil Primary Terminal 2 | Power Source (-) |
| Buzz Coil Secondary Output | Spark Gap / Load |
To effectively utilize the information presented in a Buzz Coil Wiring Diagram, it's recommended to refer to the detailed guide provided in the following section. This resource offers comprehensive explanations and practical examples to enhance your understanding.